DB3F and DF-Toolkit
The Database Forensic File Format (DB3F) is a storage format for database forensic artifacts. DB3F was designed to abstract the specifics of DBMS storage engines for users unfamiliar with DBMS internals and guide the development of database carving tools. The Database Forensic Toolkit (DF-Toolkit) is a toolkit to view and search data stored in DB3F. DF-Toolkit was designed to allow users to not only search and view data stored and queried as table records, but also metadata that helps describe the forensic state of data.
Overview: How Does DF-Toolkit Work?
Database carving tools (red), such as DBCarver, return output in DB3F (green). DB3F files are filtered and searched using DF-Toolkit (green), which stores filtered results in DB3F. DB3F files are then either directly reported to the end user or passed to further advanced analytic applications (purple).
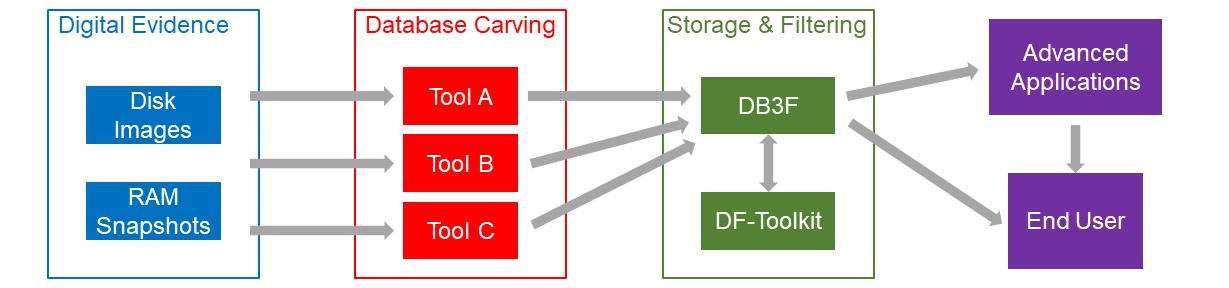
The introduction of a standardized intermediate format and a comprehensive toolkit for database forensics benefits the community in two important ways. First, it streamlines the addition of new tools on either side of the flow chart. With the introduction of a new database carving tool (e.g., Tool D), users would benefit from all available advanced applications that support DB3F. Similarly, any newly developed advanced application can trivially process output from any carving tool that supports DB3F output. The second benefit is the explicit documentation and built-in reproducibility of the analyses process and outcomes, bringing a scientific approach to digital forensics.
Examples
DB3F: Datbase Forensic File Format
Each DB3F file stores a series of JSON objects. The first line in a DB3F file contains a JSON object that serves as a header. Every other line in the DB3F file contains a JSON object that represents a database page. The file header and page fields are describe on pages 4 - 6 of DB3F publication. An example DB3F file can be downloaded from DB3F download. Note that we used DBCarver to generate the DB3F file.

Database Forensic Toolkit
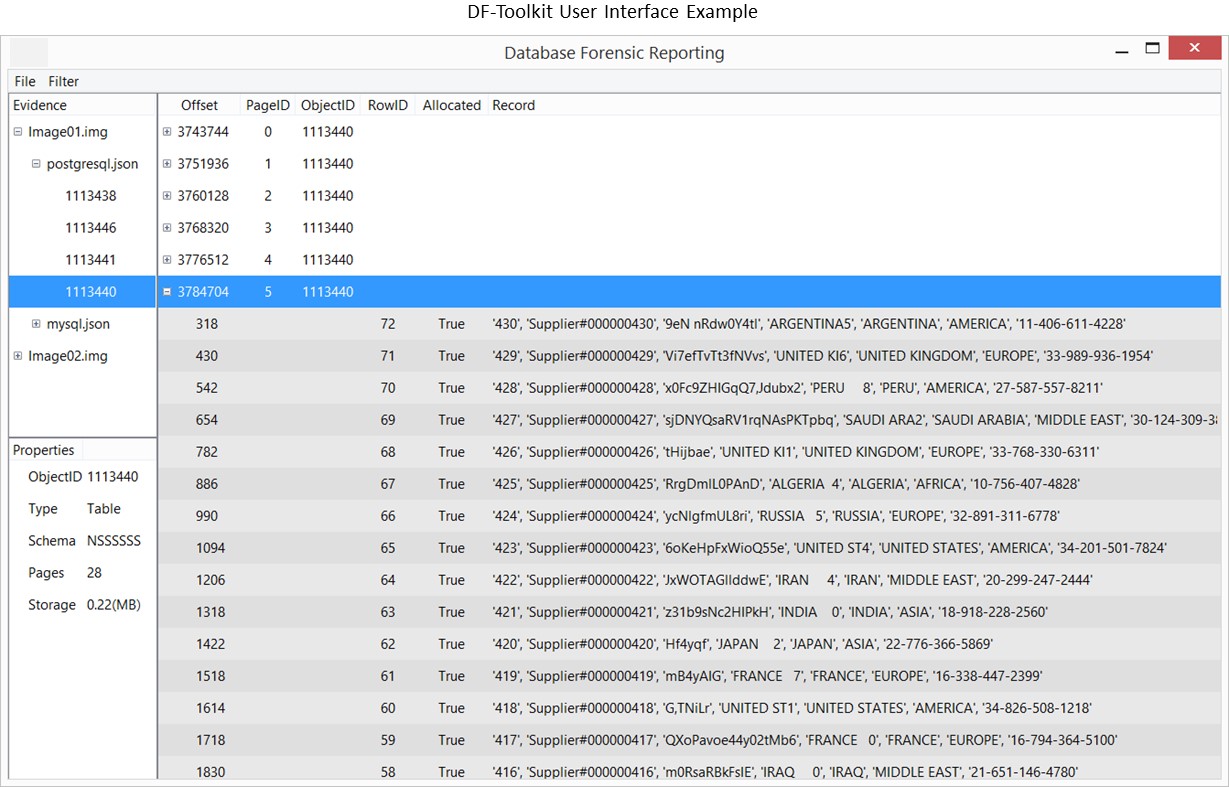
DF-Toolkit can be used to view and filter database forensic artifacts stored in DB3F. Pages 6 - 9 of DF-Toolkit publication describe how metadata and data are filtered and searched. An DF-Toolkit prototype can be downloaded from DF-Toolkit download. Note that DF-Toolkit requires DB3F files.
Literature
-
DB3F & DF-Toolkit: The Database Forensic File Format and the Database Forensic Toolkit, DFRWS 2019.
The majority of sensitive and personal user data is stored in different Database Management Systems (DBMS). For example, Oracle is frequently used to store corporate data, MySQL serves as the back-end storage for most webstores, and SQLite stores personal data such as SMS messages on a phone or browser bookmarks. Each DBMS manages its own storage (within the operating system), thus databases require their own set of forensic tools. While database carving solutions have been built by multiple research groups, forensic investigators today still lack the tools necessary to analyze DBMS forensic artifacts. The unique nature of database storage and the resulting forensic artifacts require established standards for artifact storage and viewing mechanisms in order for such advanced analysis tools to be developed.
In this paper, we present 1) a standard storage format, Database Forensic File Format (DB3F), for database forensic tools output that follows the guidelines established by other (file system) forensic tools, and 2) a view and search toolkit, Database Forensic Toolkit (DF-Toolkit), that enables the analysis of data stored in our database forensic format. Using our prototype implementation, we demonstrate that our toolkit follows the state-of-the-art design used by current forensic tools and offers easy-to-interpret database artifact search capabilities.
Team
- Alexander Rasin
- James Wagner
- Karen Heart
- Tanu Malik
- Jonathan Grier